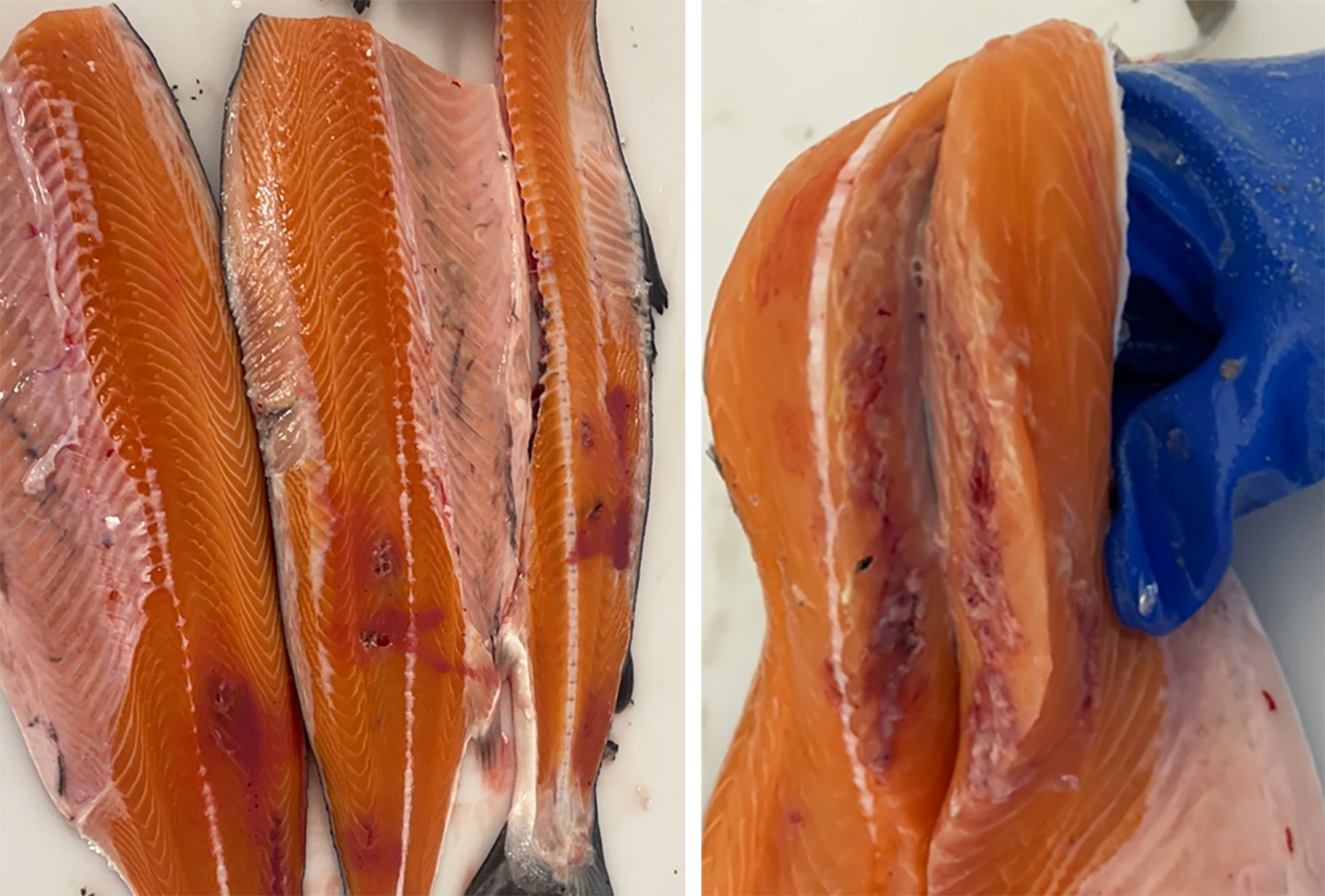
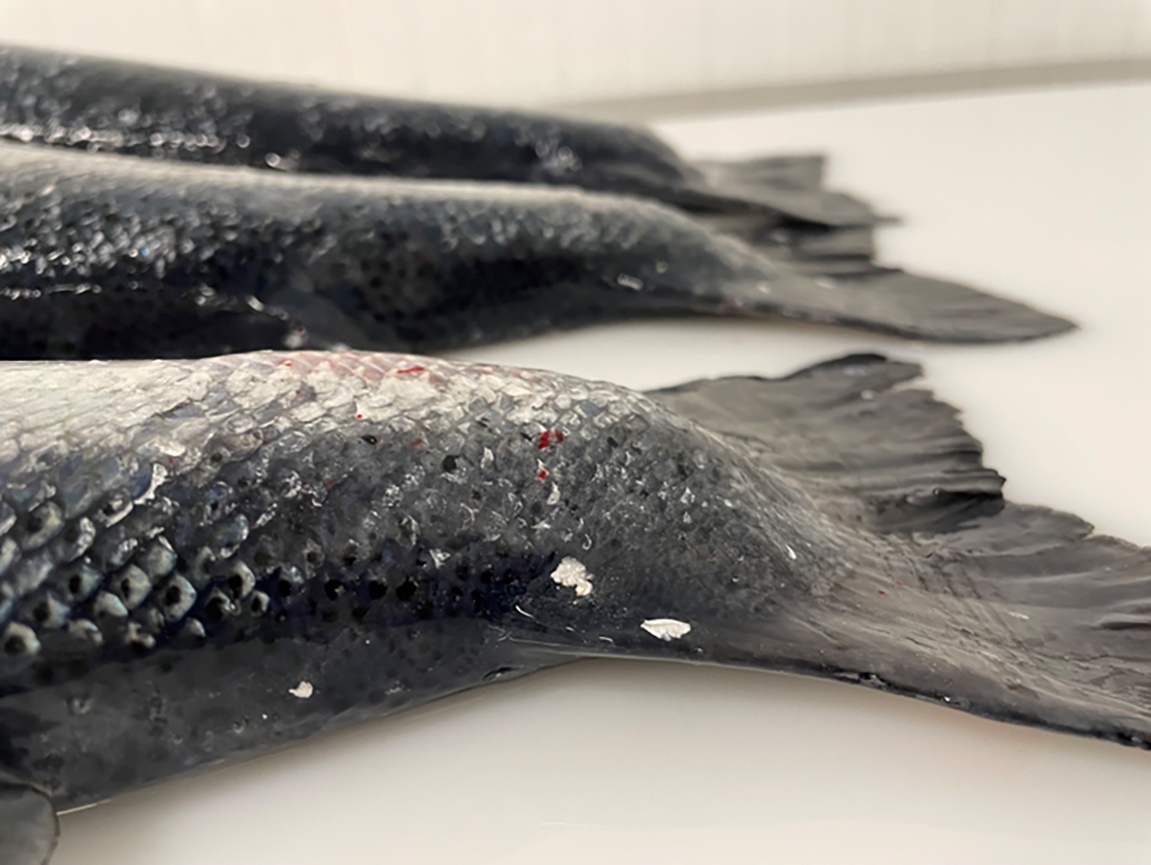
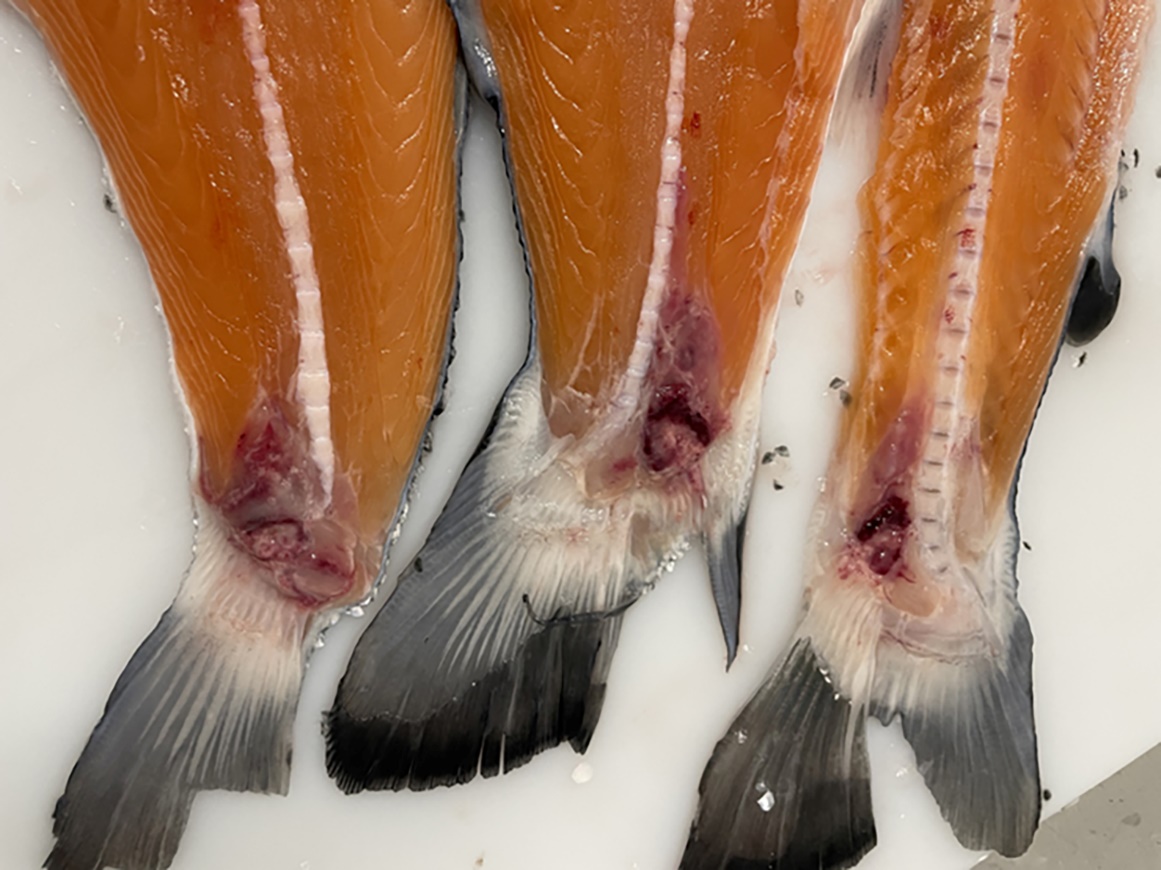
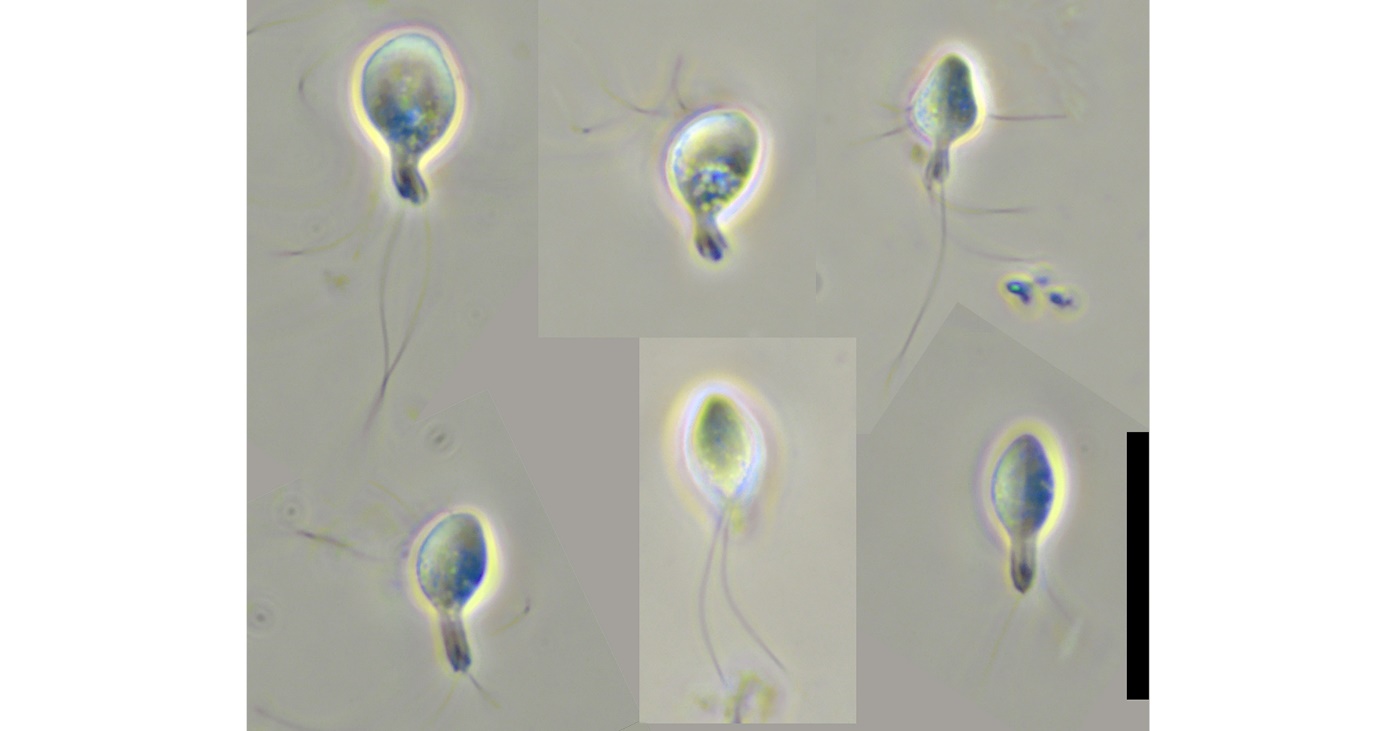
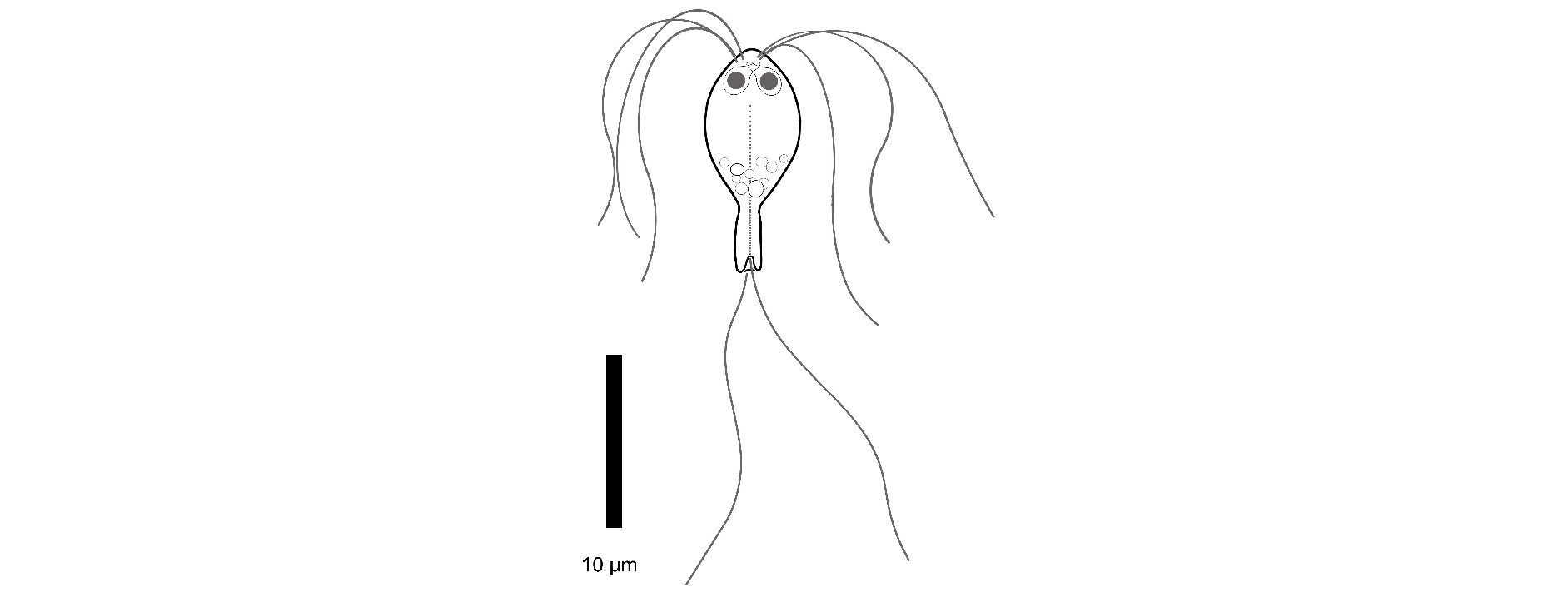
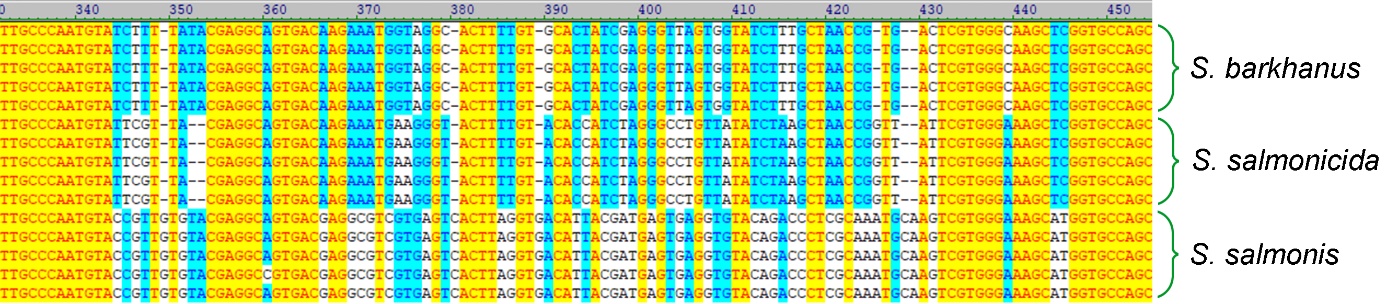
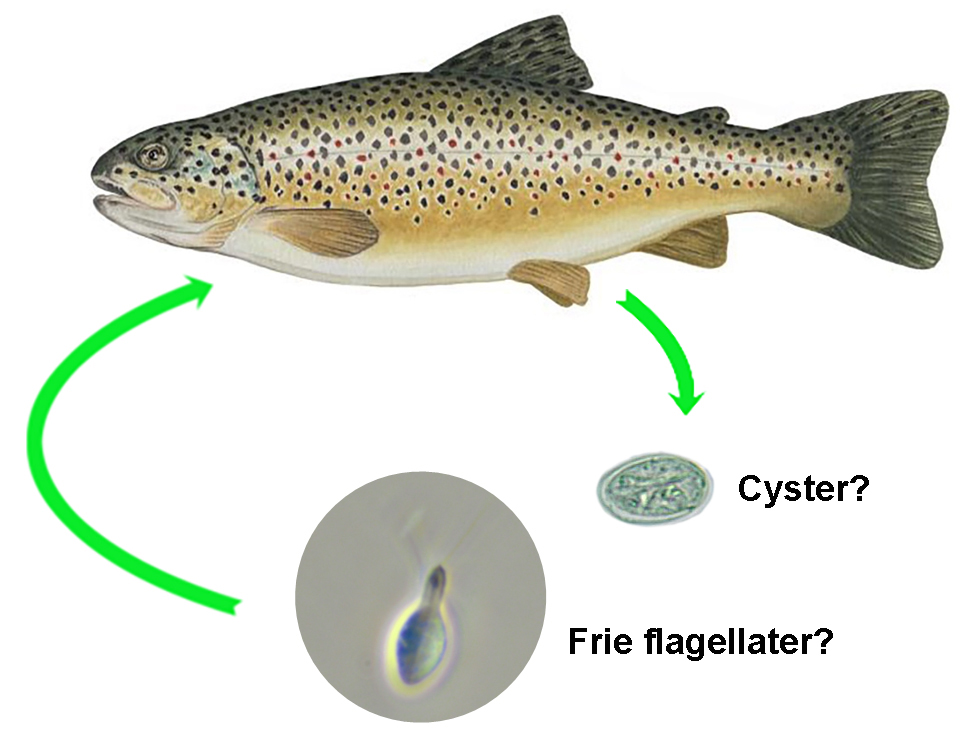
19 - Referanser
1. Dobell C (1920) The discovery of the intestinal Protozoa of man. Proc R Soc Med 13: 1-15.
2. Seligo A (1887) Untersuchungen über Flagellaten. Beiträge zur Biologie der Pflanzen 4(2): 145-180.
3. Moore E (1922) Octomitus salmonis, a new species of intestinal parasite in trout. T Am Fish Soc 52: 74-97.
4. Schmidt W (1920) Untersuchungen über Octomitus intestinalis truttae. Archiv für Protistenkunde 40: 253-289.
5. Mo TA, Poppe TT, Iversen L (1990) Systemic hexamitosis in salt-water reared Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Bull Eur Ass Fish Pathol 10: 69-70.
6. Moe TA, Poppe T, Håstein T (1990) Encellede parasitter (Protozoa). In: Poppe TT, ed. Fiskehelse Sykdommer, behandling, forebygging . John Griegs Forlag; 228-239.
7. Fard MRS, Jørgensen A, Sterud E, Bleiss W, Poynton SL (2007) Ultrastructure and molecular diagnosis of Spironucleus salmonis (Diplomonadida) from rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss in Germany. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 75(1): 37-50.
8. Jørgensen A, Sterud E (2006) The marine pathogenic genotype of Spironucleus barkhanus from farmed salmonids redescribed as Spironucleus salmonicida n. sp. J Eukaryot Microbiol 53: 531-541.
9. Lavier G (1936) Sur la structure des Flagellés du genre Hexamita Duj. C R Soc Biol 121: 1177-1181.
10. Poynton SL, Sterud E (2002) Guidelines for species descriptions of diplomonad flagellates from fish. Journal of Fish Diseases 25: 15-31.
11. Lom J, Dykova I (1992) Protozoan parasites of fishes. vol 26. Developments in Aquaculture and Fisheries Science. Elsevier; 315.
12. Brugerolle G (1974) Contribution a l’étude cytologique et phylétique des diplozoaires (Zoomastigophorea, Diplozoa, Dangeard 1910). III. Etude ultrastructurale du genre Hexamita (Dujardin 1836). Protistologica 10: 83-90.
13. Brugerolle G (1975) Contribution a l’étude cytologique et phylétique des diplozoaires (Zoomastigophorea, Diplozoa, Dangeard 1910). VI. Charactères généraux des diplozoaires. Protistologica 11: 111-118.
14. Brugerolle G, Joyon L, Oktem N (1973) Contribution a l’étude cytologique et phylétique des diplozoaires (Zoomastigophorea, Diplozoa, Dangeard 1910). II. Etude ultrastructurale du genre Spironucleus (Lavier 1936). Protistologica 9: 495-502.
15. Vickerman K (1990) Phylum Zoomastigina Class Diplomonadida. In: Margulis L, Corliss JO, Melkonian M, Chapman DJ, eds. Handbook of Protoctista: The Structure, Cultivation, Habitats and Life Histories of the Eukaryotic Microorganisms and their Descendants. Jones and Bartlett Publishers; 200-210.
16. Brugerolle G (1991) Flagellar and cytoskeletal systems in amitochondrial flagellates: Archamoeba, Metamonada and Parabasalia. Protoplasma 164: 70-90.
17. Ástvaldsson Á (2019) Pathogenesis and cell biology of the salmon parasite Spironucleus salmonicida. THESIS, PhD, Uppsala University:
18. Roxström-Lindquist K, Jerlström-Hultqvist J, Jørgensen A, Troell K, Svärd SG, Andersson JO (2010) Large genomic differences between the morphologically indistinguishable diplomonads Spironucleus barkhanus and Spironucleus salmonicida. BMC Genomics 11(258):
19. Xu F, Jiménez-González A, Kurt Z, Ástvaldsson Á, Andersson JO, Svärd SG (2022) A chromosome-scale reference genome for Spironucleus salmonicida. Scientific Data 9:585: (doi:10.1038/s41597-022-01703-w)
20. Wiśniewska MM, Salomaki ED, Silberman JD, Terpis KX, Mazancová E, Táborský P, Jinatham V, Gentekaki E, Čepička I, Kolisko M (2024) Expanded gene and taxon sampling of diplomonads shows multiple switches to parasitic and free-living lifestyle. BMC Biology 22:217: (doi:10.1186/s12915-024-02013-w)
21. Jackson GA, Livingston RS, Riley LK, Livingston BA, Franklin CL (2013) Development of a PCR assay for the detection of Spironucleus muris. Journal of the American Association for Laboratory Animal Science 52(2): 165-170.
22. Miller KM, Gardner IA, Vanderstichel R, Burnley T, Schulze AD, Li S, Tabata A, Kaukinen KH, Ming TJ, Ginther NG (2016) Report on the performance evaluation of the Fluidigm BioMark platform for high-throughput microbe monitoring in salmon. Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat (CSAS), Research Document 2016/038, Pacific Region 2016(038):
23. Mizuno K, Urawa S, Katsumata Y, Morishita T, Minowa Y, Ban M (2020) Quantitative analysis of diplomonad flagellate Spironucleus salmonis infection in intestines of hatchery and wild salmonid fishes in Hokkaido. Fish Pathology 55(3): 61-70. (doi:doi.org/10.3147/jsfp.55.61)
24. Guo FC (2006) Spironucleus spp. and experimental spironucleosis in salmonids. University of Guelph;
25. Guo FC, Woo PTK (2004) Experimental infections of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar with Spironucleus barkhanus. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 61: 59-66.
26. Kent ML, Ellis J, Fournie JW, Dawe SC, Bagshaw JW, Whitaker DJ (1992) Systemic hexamitid (Protozoa: Diplomonadida) infection in seawater pen-reared chinook salmon Oncorhynchus tshawytscha. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 14: 81-89.
27. Alfjorden A (2018) Experimental Spironucleus infections in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Hidden secrets of the life cycle of Spironucleus salmonicida revealed. Thesis, MSc, Uppsala Universitet:
28. Kulda J, Lom J (1964) Remarks on the diplomastigine flagellates from the intestine of fishes. Parasitology 54: 753-762.
29. Sommerhaug E (1995) Kultivering av mikroparasitten Hexamita sp. in vitro og in vivo i atlantisk laks (Salmo salar), og påvisning av antistoffaktivitet mot parasitten i atlantisk laks. cand. scient. Tromsø;
30. Tojo JL, Santamarina MT (1998) Oral pharmacological treatments for parasitic diseases of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. I: Hexamita salmonis. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 33: 51-56.
31. Uzmann JR, Hayduk SH (1963) In vitro culture of the flagellate protozoan Hexamita salmonis. Science 140: 290-292.
32. Uzmann JR, Paulik GJ, Hayduk SH (1965) Experimental hexamitiasis in juvenile coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) and steelhead trout (Salmo gairdneri). T Am Fish Soc 94(1): 53-61.
33. Williams CF (2013) Life cycle, biochemistry and chemotherapy of Spironucleus vortens. Thesis, PhD, School of Biosciences, Cardiff University:
34. Williams CF, Vacca AR, Lloyd D, Schelkle B, Cable J (2013) Non-invasive investigation of Spironucleus vortens transmission in freshwater angelfish Pterophyllum scalare. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 105(3): 211-223. (doi:Doi 10.3354/Dao02618)
35. Woo PTK, Poynton SL (1995) Diplomonadida, Kinetoplastida and Amoebida (Phylum Sarcomastigophora). In: Woo PTK, ed. Fish Diseases and Disorders Vol I Protozoan and metazoan infections. CAB International; 27-96.
36. Leitsch D, Williams CF, Hrdy I (2018) Redox pathways as drug targets in microaerophilic parasites. Trends in Parasitology 34(7): 576-586.
37. Lloyd D, Williams CF (2014) Comparative biochemistry of Giardia, Hexamita and Spironucleus: Enigmatic diplomonads. Molecular & Biochemical Parasitology 197: 43–49.
38. Williams CF, Yarlett N, Aon MA, Lloyd D (2014) Antioxidant defences of Spironucleus vortens: Glutathione is the major non-protein thiol. Molecular & Biochemical Parasitology 196: 45–52.
39. Stairs CW, Kokla A, Ástvaldsson Á, Jerlström-Hultqvist J, Svärd S, Ettema TJG (2019) Oxygen induces the expression of invasion and stress response genes in the anaerobic salmon parasite Spironucleus salmonicida. BMC Biology 17:19: (doi:10.1186/s12915-019-0634-8)
40. Aguilar-Diaz H, Carrero JC, Argüello-Garcia R, Laclette JP, Morales-Montor J (2011) Cyst and encystment in protozoan parasites: optimal targets for new life-cycle interrupting strategies? Trends in Parasitology 27(10): 450-458.
41. Benchimol M, De Souza W (2011) The ultrastructure of Giardia during growth and differentiation. In: Lujan HD, Svärd S, eds. Giardia A Model Organism Springer. Springer; 141-160:chap 9.
42. Kunstyr I (1977) Infectious form of Spironucleus (Hexamita) muris: banded cysts. Laboratory Animals 11: 185-188.
43. Brugerolle G, Kunstyr I, Senaud J, Friedhoff KT (1980) Fine structure of trophozoites and cysts of the pathogenic diplomonad Spironucleus muris. Z Parasitekd 62: 47-61.
44. Uldal A (1996) Life cycle observations on Hexamita salmonis from rainbow trout intestine. In vitro studies. Bull Eur Ass Fish Pathol 16: 112-114.
45. Karlsbakk E Upubliserte observasjoner.
46. Xu F, Jerlström-Hultqvist J, Einarsson E, Astvaldsson A, Svärd SG, Andersson JO (2014) The genome of Spironucleus salmonicida highlights a fish pathogen adapted to fluctuating environments. PLoS Genet 10(2): e1004053. (doi:doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004053)
47. Helsø M (2024) Miljøoverlevelse hos Spironucleus salmonicida - parasitten som forårsaker systemisk spironukleose hos oppdrettslaks. MSc Thesis, BiO, Univ Bergen, :
48. Wood AM, Smith HV (2005) Spironucleosis (Hexamitiasis, Hexamitosis) in the ring-necked pheasant (Phasianus colchicus): Detection of cysts and description of Spironucleus meleagridis in stained smears. Avian Diseases 49(1): 138-143.
49. Lavier G (1936) Sur quelques flagelles intestinaux de Poissons marins. Ann Parasitol 14: 278-289.
50. Millet C (2009) Growth, metabolism, ultrastructure and chemotherapy of Spironucleus vortens. PhD Thesis, Cardiff University:
51. Poppe TT, Mo TA, Iversen L (1992) Disseminated hexamitosis in sea-caged Atlantic salmon Salmo salar. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 14: 91-97.
52. Kent ML (1998) Protozoa and Myxozoa. In: Kent ML, Poppe TT, eds. Diseases of seawater netpen-reared salmonid fishes. Fisheries & Oceans; 49-67.
53. Jerlström-Hultqvist J, Einarsson E, Xu F, Hjort K, Ek B, Steinhauf D, Hultenby K, Bergquist J, Andersson JO, Svärd SG (2013) Hydrogenosomes in the diplomonad Spironucleus salmonicida. Nature Communications 4:2493: 9 p. (doi:DOI: 10.1038/ncomms3493)
54. Ástvaldsson Á, Hultenby K, Svärd SG, Jerlström-Hultqvist J (2019) Proximity staining using enzymatic protein tagging in diplomonads. mSphere 4(2): e00153-19.
55. Mo TA, Poppe TT (1992) Hexamitose i nordnorske oppdrettsanlegg: en tilfeldighet eller et nytt alvorlig problem. Norsk Fiskeoppdrett : 48-50.
56. Jørgensen A, Torp K, Bjørland MA, Poppe TT (2011) Wild Arctic char Salvelinus alpinus and trout Salmo trutta : hosts and reservoir of the salmonid pathogen Spironucleus salmonicida (Diplomonadida; Hexamitidae). Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 97(1): 57-63. (doi:Doi 10.3354/Dao02404)
57. Mizuno S, Urawa S, Katsumata Y, Morishita T, Ban M (2020) Ultrastructural and molecular phylogenetic identification of the diplomonad flagellate Spironucleus salmonis infecting hatchery-reared salmonid fishes in Hokkaido. Fish Pathol 55(1): 8-17.
58. Denikina N, Kondratov I, Belkova N, Sokolov S (2019) The phylogenetic position of Spironucleus sp. (Diplomonadida: Hexamitidae) from the Intestine of Chinese sleeper Perccottus glenii Dybowski, 1877 (Actinopterygii: Odontobutidae). Acta Parasitologica 64: 347–351.
59. Denikina N, Nebesnykh I, Maikova O, Dzyuba E, Belkova N (2016) Genetic diversity of Diplomonadida in fish of the genus Coregonus from Southeastern Siberia. Acta Parasitologica 61: 299-306. (doi:10.1515/ap-2016-0040)
60. NVI (2023) Fiskehelserapporten 2022. Veterinærinstituttet rapportserie 2023(5a):
61. Jørgensen A, Sterud E (2007) Phylogeny of Spironucleus (Eopharyngia : Diplomonadida : Hexamitinae). Protist 158: 247-254.
62. Jørgensen A, Alfjorden A, Henriksen K, Sterud E (2007) Phylogenetic analysis of the SSU rRNA gene from the piscine diplomonad Spironucleus torosus (Diplomonadida : Hexamitinae). Folia Parasitologica 54: 277-282.
63. Chapman JM (2020) Factors influencing infectious agent communities and infection burden in free-ranging migratory adult salmonids across Canada. PhD Thesis, Carleton University, Ottawa, Ontario:
64. Karlsbakk E, Sandlund N, Austgulen MH, Mæhle S, Berg-Rolness H, Skår C, Lofnes A, Aga J, Ghebretnsae DB, Nordbø J, Sengee A, Røttingen TB, Kvamme BO (2025) Verter og vektorer i sjø for Spironucleus salmonicida, mikroparasitten som forårsaker systemisk spironucleose i oppdrettslaks. Abstract, Frisk Fisk 2025 Tromsø:
65. Balta F, Balta ZD, Akhan S (2019) Seasonal distribution of protozoan parasite infections in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) farms in the eastern Black Sea of Turkey. Bulletin of the European Association of Fish Pathologists 39(1): 31-39.
66. Bel’kova NL, Dzyuba EV, Sukhanova EV (2008) Molecular-genetic detection of a nonpathogenic genotype of Spironucleus barkhanus (Diplomonadida: Hexamitidae) in the black Baikal grayling (Thymallus arcticus baicalensis Dybowski, 1874). Biology Bulletin 35(2): 219-221.
67. Bjørland M, Torp K (2009) Spironucleosis in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). MSc. Norwegian School of Veterinary Science;
68. Denikina N, Nebesnykh IA, Kondratov IG, Khanaev IV, Dzyuba EV (2018) Representatives of Diplomonadida in fishes of East Siberia. Limnology and Freshwater Biology 2018: 103-106.
69. Kristmundsson A, Richter SD (2009) Parasites of resident Arctic charr, Salvelinus alpinus, and brown trout, Salmo trutta, in two lakes in Iceland. Icel Agric Sci 22: 5-18.
70. Andersson KA (1964) Fisksjukdommar och fiskparasiter. In: Andersson KA, ed. Fiskar och Fiske i Norden. 3 ed. Bokförlaget Natur och Kultur; 695-710.
71. Buchmann K, Uldal A (1996) Temperature, pH and bile dependent in vitro cultivation of Hexamita salmonis from rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss intestine. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 24: 169-172.
72. Buchmann K, Uldal A, Lyholt HCK (1995) Parasite infections in Danish trout farms. Acta vet scand 36: 283-298.
73. Bylund G, Fagerholm H-P (1984) Fisksjukdommar. Yrkesutbildingsstyrelsen Statens Tryckericentral; 108.
74. Shulman BS, Ieshko EP (2005) Parasite fauna of Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus) and greyling (Thymallus thymallus) in some lakes from northern Finland. Lososevidnye Ryby Vostochnoi Fennoskandii, Petrozavodsk: 195-197.
75. Kirjusina M, Vismanis K (2007) Checklist of the parasites of fishes of Latvia. FAO Fisheries Technical Paper 369/3: 106 p.
76. Poynton SL (1986) Distribution of the flagellate Hexamita salmonis Moore, 1922 and the microsporidian Loma salmonae Putz, Hoffman and Dunbar, 1965 in brown trout, Salmo trutta L., and rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson, in the River Itchen (U.K.) and three of its fish farms. J Fish Biol 29: 417-429.
77. Poynton SL, Fard MRS, Jenkins J, Ferguson HW (2004) Ultrastructure of Spironucleus salmonis n. comb. (formerly Octomitus salmonis sensu Moore 1922, Davis 1926, and Hexamita salmonis sensu Ferguson 1979), with a guide to Spironucleus species. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 60: 49-64.
78. Lom J, Dyková I (1989) Protozoární paraziti uzitkovych ryb [Protozoan parasites of commercial fish]. Vydal. Cesky rybarsky svaz ve Statnim zemedelskem nakladatelstvi [Czech Fishermen's Association in the State Agricultural Publishing House]; 102.
79. Dyková I, Lom J (2007) Histopathology of protistan and myxozoan infections in fishes. Academia; 219.
80. Guz L, Puk K (2015) First molecular identification of Spironucleus salmonis (Diplomonadida) from diseased rainbow trout Oncorchynchus mykiss in Poland. Med Weter 71(8): 497-499.
81. Becker CD (1977) Flagellate parasites of fish. In: Kreier, ed. Parasitic Protozoa. Academic Press; 357-416.
82. Skenderovic I, Adrovic A, Jazic A, Zuko A, Hadzimustafic E (2020) Review of freshwater fish parasitofauna of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Biologia 76(2): (doi:10.2478/s11756-020-00565-0)
83. Imamovic V (1986) Parasites and parasitoses in the fish in some salmonid hatcheries in Bosnia-Hercegovina I. Ichthyobodiosis and hexamitosis. Veterinaria 35: 47-66.
84. Grupcheva GI, Golemansky VG, Lom J, Dykova I, Pavlaskova M (1986) Protozoan parasites of the fish in some Bulgarian reservoirs. III. Ichthyoparasiting fauna in the "Dospat" reservoir. Acta Zoologica Bulgarica 31: 37-41.
85. Busarova OU (2024) Parasitofauna of Dolly Varden Salvelinus malma complex in Kamchatka. The researchers of the aquatic biological resources of Kamchatka and the north-west part of the Pacifi Ocean 75: 22-52. (doi:10.15853/2072-8212.2024.75.22-52)
86. Konovalov SM (1975) Differentiation of local populations of sockeye salmon Oncorhynchus nerka (Walbaum). University of Washington, Publications in Fisheries, new series (Sagen, LV, transl) 6: 1-290.
87. Zaika VE (1965) The parasitofauna of fish in Lake Baikal. Izdatel’stvo "Nauka"; 106.
88. Barskaya YY, Ieshko EP (2005) Parasite faunas of salmonoids from the Paanajarvi -Oulanga lake-river system and its formation patterns. Lososevidnye Ryby Vostochnoi Fennoskandii. 13-22.
89. Petrushevskii GK, Pozdnyakova (Vikhrova) MN, Shul'man SS (1957) The parasites of fish from Braslav Lakes in Belorussia. In: Petrushevskii GK, ed. Parasites and diseases of fish. Otdel Rybnoi Promyshlennosti Gosplana RSFSR; 336-338. vol. Bulletin of the All/Union Scientific Research Institute of Lake and River Fisheries.
90. Vinnichenko LN, Zaika VE, Timofeev VA, Shtein GA, Shulman SS (1971) Parasitic Protozoa of fishes from the Amur river basin. Parazitologicheskii Sbornik Zoologicheskogo Instituta Akademii Nauk SSSR 25: 10-40.
91. Pazooki J, Masoumian M (2012) Synopsis of the parasites in Iranian freshwater fishes. Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences 11(3): 570-591.
92. Ogut H, Parlak R (2014) Hexamitiasis leads to lower metabolic rates in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum) juveniles. J Fish Dis 37: 1013-1020.
93. Timur G, Karatas S, Akayli T, Ercan MD, Yardimci RE (2009) A histopathological study of hexamitiasis in farmed rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fry in Turkey. Bulletin of the European Association of Fish Pathologists 29(3): 104-108.
94. Hoffmann GL (1999) Parasites of North American freshwater fishes. 2 ed. Comstock Publishing Associates; 539.
95. Hare GM, Frantsi C (1974) Abundance and potential pathology of parasites infecting salmonids in Canadian maritime hatcheries. Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada 31: 1031-1036.
96. Love MS, Moser M (1983) A checklist of parasites of California, Oregon, and Washington marine and estuarine fishes. NOAA Technical Report NMFS SSRF 777: 1-576.
97. Wood JW (1979) Diseases of Pacific salmon; Their prevention and treatment. 3 ed. State of Washington, Department of Fisheries, Hatchery Division; 82.
98. Moore E (1923) The life-history of Octomitus salmonis, an intestinal flagellate of trout. Anat Rec 26: 358-359.
99. Davis HS (1926) Octomitus salmonis, a parasitic flagellate of trout. Bull US Bur Fish 42: 9-26.
100. Davis HS (1925) The intestinal protozoa of trout. T Am Fish Soc 5 (1924): 57-63.
101. Davis HS (1953) Culture and diseases of game fishes. Univ. California Press; 332.
102. Turovskij A (1985) Parasitofauna of fish in the southern Gulf of Finland. Finnish Fish Res 6: 106-111.
103. Sterud E, Poppe T, Bornø G (2002) Programkonferanse Havbruk og Villaks, Norges Forskningsråd; 46.
104. Sterud E, Poppe T, Bornø G (2003) Intracellular infection with Spironucleus barkhanus (Diplomonadida : Hexamitidae) in farmed Arctic char Salvelinus alpinus. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 56: 155-161.
105. Sterud E, Poppe TT, Bornø G (2003) Systemic and intracellular infection with Spironucleus barkhanus in farmed Arctic char, Salvelinus alpinus. 6 ISAFP Bloemfontein, South Africa (Sixth International Symposium on fish Parasites, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa): 31.
106. Lofnes A (2025) Spironucleus salmonicida – histopatologi og vevstropisme i ulike vertsarter. THESIS, MSc, BiO, UiB:
107. Poppe TT, Mo TA (1993) Systemic, granulomatous hexamitosis of farmed Atlantic salmon: Interaction with wild fish. Fisheries Research 17: 147-152.
108. Alfjorden A, Astvaldsson A, Jansson E, Svärd S (2019) Experimental challenge of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) with the diplomonad parasite Spironucleus salmonicida to characterize the infection cycle. http://wwwdiva-portalorg/smash/recordjsf?pid=diva2%3A1295066& :
109. Ferguson HW (1979) Scanning and transmission electron microscopical observations on Hexamita salmonis (Moore, 1922) related to mortalities in rainbow trout fry Salmo gairdneri Richardson. J Fish Dis 2: 57-67.
110. Millet COM, Williams CF, Hayes AJ, Hann AC, Cable J, Lloyd D (2013) Mitochondria-derived organelles in the diplomonad fish parasite Spironucleus vortens. Experimental Parasitology 135: 262–273.
111. Lloyd D, Chapman A, Ellis JE, Hillman K, Paget TA, Yarlett N, Williams AG (2021) Oxygen levels are key to understanding “anaerobic” protozoan pathogens with micro-aerophilic lifestyles. Advances in Microbial Physiology 79: 163-240.
112. Lloyd D, Millet CO, Williams CF, Hayes AJ, Pope SJA, Pope I, Borri P, Langbein W, Olsen LF, Isaacs MD, Lunding A (2020) Functional imaging of a model unicell: Spironucleus vortens as an anaerobic but aerotolerant flagellated protist. Advances in Microbial Physiology 76: 41-79.
113. Millet COM, Lloyd D, Coogan MP, Rumsey J, Cable J (2011) Carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism of Spironucleus vortens. Experimental Parasitology (129): 17–26.
114. Moroff T (1904) Beitrag zur Kenntnis einiger Flagellaten. Arch Protistenkd 3: 69-106.
115. Davis HS (1923) Observations on an intestinal flagellate of trout. Journal of Parasitology 9(3): 153-160.
116. Uzmann JR (1963) The Hexamita (=Octomitus) problem: a preliminary report. Progr Fish Cult 25(3): 141-143.
117. Morrison CM (1987) Histology of the Atlantic Cod, Gadus morhua: An Atlas. Part one. Digestive tract and associated organs. Can Spec Publ Fish Aquat Sci 98: 219 p.
118. Poynton SL, Morrison CM (1990) Morphology of diplomonad flagellates: Spironucleus torosa n. sp. from Atlantic cod Gadus morhua L., and haddock Melanogrammus aeglefinus (L.) and Hexamita salmonis Moore from brook trout Salvelinus fontinalis (Mitchill). J Protozool 37: 369-383.
119. Guo FC, Woo PTK (2004) Detection and quantification of Spironucleus barkhanus in experimentally infected Atlantic salmon Salmo salar. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 61: 175-178.
120. Einszporn-Orecka T (1979) Flagellates Spironucleus anguillae sp. n. parasites of eel (Anguilla anguilla L.). Acta Protozoologica 18: 237-241.
121. Molnár K (1974) Data on the “octomitosis” (spironucleosis) of cyprinids and aquary fishes. Acta Vet Acad Sci Hungaricae 24: 99-106.
122. Ferguson HW, Moccia RD (1980) Disseminated hexamitiasis in Siamese fighting fish. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association 177: 854-857.
123. Poynton SL, Fraser W, Francis-Floyd R, Rutledge P, Reed P, Nerad TA (1995) Spironucleus vortens n. sp. from the freshwater angelfish Pterophyllum scalare: morphology and culture. J Eukaryot Microbiol 42: 731-742.
124. Amlacher E (1972) Taschenbuch der Fischkrankheiten für Veterinärmediziner und Biologen. Gustav Fischer Verlag; 378.
125. Mankhakhet S, Suanyuk N, Tantikitti C, Phromkunthong W, Kiriratnikom S, Lerssutthichawal T, Viriyapongsutee B (2012) Diplomonad flagellates of some ornamental fish cultured in Thailand. Songklanakarin J Sci Technol 34(5): 487-494.
126. Paull GC, Matthews RA (2001) Spironucleus vortens, a possible cause of hole-in-the-head disease in cichlids. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 45: 197-202.
127. Mo TA, Poppe TT, Appleby C (1993) Kohabiteringsforsøk med fire ulike arter laksefisk og en encellet parasitt i slekten Hexamita . Norsk Veterinærtidsskrift 105: 349-353.
128. Kvamme BO, Mæhle S, Berg-Rolness H, Austgulen MH, Sengee A, Ghebretnsae DB, Nordbø J, Skår C, Penaranda MMD, Skaftnesmo KO, Karlsbakk E (2025) Utprøving av fem ulike Spironucleus salmonicida smittemodellar for post-smolt laks i sjøvatn. Rapport fra havforskningen 2025(25):
129. Poppe TT, Mo TA (1992) Hexamita - parasitten gir sykdom hos oppdrettslaks i sjø. Norsk Fiskeoppdrett 1992: 26-28.
130. Bruno D, Noguera P, Poppe TT (2013) A Colour Atlas of Salmonid Diseases. Springer.
131. Sterud E, Poppe TT, Larsen T, Iversen L (2002) Men Spironucleus var ikke død. Norsk Fiskeoppdrett : 38-40.
132. Markeng D (2001) Spironukleose i Finnmark. Aquavisa 1(3): 2-3.
133. Kyst.no (2022) Parasitt har gitt betydelige tap i form av dødelighet og destruksjon av fisk - FHF lyser nå ut midler. Kystno Tirsdag 18. oktober 2022 - 14:17:
134. Furuset A (2024) Parasitt kostet lakseselskapet 900 mill. IntraFish Publisert 22 februar 2024, kl 1102 :
135. Lie K-I, Wisløff H, Alarcon M, Nylund S (2022) Spironukleose hos atlantisk laks. Norsk Veterinærtidsskrift 134(6): 400-401.
136. Tjessem AV (2024) Upubliserte observasjoner 2024.
137. NVI (2024) Fiskehelserapporten 2023. Veterinærinstituttet rapportserie 2024(8a):
138. Karlsbakk E, Fjær MA, Moore LJ, Skaala Ø, Madhun AS (2020) Pukkellaks og villaks, patogener og parasitter - hva vet vi? Norsk Fiskeoppdrett 2020(1): 60-63.
139. Fjær MA (2019) Pukkellaks ( Oncorhynchus gorbuscha ) tatt på Vestlandet. - Hvilke parasitter og infeksjoner bærer de på? THESIS Univ Bergen, Dept Biosciences :
140. Johansen L-H, Brenne H (2024) Effekten av ulike desinfeksjonsstrategier på Spironucleus salmonicida . AP 2.1. Nofima Rapport 2024(25):
141. Poppe TT, Mo TA, Torgersen Y (1993) Effekt av ulike behandlingsmidler på en encellet parasitt i slekten Hexamita isolert fra oppdrettslaks. Norsk Veterinærtidsskrift 105: 835-838.
142. Kayis S, Ozcelep T, Capkin E, Altinok I (2009) Protozoan and metazoan parasites of cultured fish in Turkey and their applied treatments. The Israeli Journal of Aquaculture – Bamidgeh 61(2): 93-102.
143. Williams CF, Lloyd D, Poynton SL, Jorgensen A, Millet COM, Cable J (2011) Spironucleus species: Economically-important fish pathogens and enigmatic single-celled eukaryotes. Journal of Aquaculture, Research & Development 2011(S2): 13 p. (doi:10.4172/2155-9546.S2-002)
144. Williams CF, Lloyd D, Kolarich D, Alagesan K, Duchene M, Cable J, Williams D, Leitsch D (2012) Disrupted intracellular redox balance of the diplomonad fish parasite Spironucleus vortens by 5-nitroimidazoles and garlic-derived compounds. Veterinary Parasitology 190: 62– 73.
145. Williams CF, Vacca AR, Lloyd D, Coogan MP, Evans G, Graz M, Cable J (2016) The redox-active drug metronidazole and thiol-depleting garlic compounds act synergistically in the protist parasite Spironucleus vortens. Molecular & Biochemical Parasitology 206: 20–28.
�
Referanser, alfabetisk.
Aguilar-Diaz H, Carrero JC, Argüello-Garcia R, Laclette JP, Morales-Montor J. Cyst and encystment in protozoan parasites: optimal targets for new life-cycle interrupting strategies? Trends in Parasitology. 2011;27(10):450-458.
Alfjorden A. Experimental Spironucleus infections in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Hidden secrets of the life cycle of Spironucleus salmonicida revealed. Thesis, MSc, Uppsala Universitet. 2018;
Alfjorden A, Astvaldsson A, Jansson E, Svärd S. Experimental challenge of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) with the diplomonad parasite Spironucleus salmonicida to characterize the infection cycle. http://wwwdiva-portalorg/smash/recordjsf?pid=diva2%3A1295066&. 2019;
Amlacher E. Taschenbuch der Fischkrankheiten für Veterinärmediziner und Biologen. Gustav Fischer Verlag; 1972:378.
Andersson KA. Fisksjukdommar och fiskparasiter. In: Andersson KA, ed. Fiskar och Fiske i Norden. 3 ed. Bokförlaget Natur och Kultur; 1964:695-710.
Ástvaldsson Á. Pathogenesis and cell biology of the salmon parasite Spironucleus salmonicida. THESIS, PhD, Uppsala University. 2019;
Ástvaldsson Á, Hultenby K, Svärd SG, Jerlström-Hultqvist J. Proximity staining using enzymatic protein tagging in diplomonads. mSphere. 2019;4(2):e00153-19.
Balta F, Balta ZD, Akhan S. Seasonal distribution of protozoan parasite infections in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) farms in the eastern Black Sea of Turkey. Bulletin of the European Association of Fish Pathologists. 2019;39(1):31-39.
Barskaya YY, Ieshko EP. Parasite faunas of salmonoids from the Paanajarvi -Oulanga lake-river system and its formation patterns. Lososevidnye Ryby Vostochnoi Fennoskandii. 2005:13-22.
Becker CD. Flagellate parasites of fish. In: Kreier, ed. Parasitic Protozoa. Academic Press; 1977:357-416.
Bel’kova NL, Dzyuba EV, Sukhanova EV. Molecular-genetic detection of a nonpathogenic genotype of Spironucleus barkhanus (Diplomonadida: Hexamitidae) in the black Baikal grayling (Thymallus arcticus baicalensis Dybowski, 1874). Biology Bulletin. 2008;35(2):219-221.
Benchimol M, De Souza W. The ultrastructure of Giardia during growth and differentiation. In: Lujan HD, Svärd S, eds. Giardia A Model Organism Springer. Springer; 2011:141-160:chap 9.
Bjørland M, Torp K. Spironucleosis in farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). MSc thesis NVH, 2009.
Brugerolle G. Contribution a l’étude cytologique et phylétique des diplozoaires (Zoomastigophorea, Diplozoa, Dangeard 1910). III. Etude ultrastructurale du genre Hexamita (Dujardin 1836). Protistologica. 1974;10:83-90.
Brugerolle G. Contribution a l’étude cytologique et phylétique des diplozoaires (Zoomastigophorea, Diplozoa, Dangeard 1910). VI. Charactères généraux des diplozoaires. Protistologica. 1975;11(1):111-118.
Brugerolle G. Flagellar and cytoskeletal systems in amitochondrial flagellates: Archamoeba, Metamonada and Parabasalia. Protoplasma. 1991;164:70-90.
Brugerolle G, Joyon L, Oktem N. Contribution a l’étude cytologique et phylétique des diplozoaires (Zoomastigophorea, Diplozoa, Dangeard 1910). II. Etude ultrastructurale du genre Spironucleus (Lavier 1936). Protistologica. 1973;9:495-502.
Brugerolle G, Kunstyr I, Senaud J, Friedhoff KT. Fine structure of trophozoites and cysts of the pathogenic diplomonad Spironucleus muris. Z Parasitekd. 1980;62:47-61.
Bruno D, Noguera P, Poppe TT. A Colour Atlas of Salmonid Diseases. Springer; 2013.
Buchmann K, Uldal A, Lyholt HCK. Parasite infections in Danish trout farms. Acta vet scand. 1995;36:283-298.
Buchmann K, Uldal A. Temperature, pH and bile dependent in vitro cultivation of Hexamita salmonis from rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss intestine. Dis aquat Org. 1996;24:169-172.
Busarova OU. Parasitofauna of Dolly Varden Salvelinus malma complex in Kamchatka. The researchers of the aquatic biological resources of Kamchatka and the north-west part of the Pacifi Ocean. 2024;75:22-52. doi:10.15853/2072-8212.2024.75.22-52
Bylund G, Fagerholm H-P. Fisksjukdommar. Yrkesutbildingsstyrelsen Statens Tryckericentral; 1984:108.
Chapman JM. Factors influencing infectious agent communities and infection burden in free-ranging migratory adult salmonids across Canada. PhD Thesis, Carleton University, Ottawa, Ontario. 2020;
Davis HS. Culture and diseases of game fishes. Univ. California Press; 1953:332.
Davis HS. Observations on an intestinal flagellate of trout. Journal of Parasitology. 1923;9(3):153-160.
Davis HS. Octomitus salmonis, a parasitic flagellate of trout. Bull US Bur Fish. 1926;42:9-26.
Davis HS. The intestinal protozoa of trout. Trans Amer Fish Soc. 1925;5 (1924):57-63.
Denikina N, Kondratov I, Belkova N, Sokolov S. The phylogenetic position of Spironucleus sp. (Diplomonadida: Hexamitidae) from the Intestine of Chinese sleeper Perccottus glenii Dybowski, 1877 (Actinopterygii: Odontobutidae). Acta Parasitologica. 2019;64:347–351.
Denikina N, Nebesnykh I, Maikova O, Dzyuba E, Belkova N. Genetic diversity of Diplomonadida in fish of the genus Coregonus from Southeastern Siberia. Acta Parasitologica. 2016;61(2):299-306. doi:10.1515/ap-2016-0040
Denikina N, Nebesnykh IA, Kondratov IG, Khanaev IV, Dzyuba EV. Representatives of Diplomonadida in fishes of East Siberia. Limnology and Freshwater Biology. 2018;2018(2):103-106.
Dobell C. The discovery of the intestinal Protozoa of man. Proc R Soc Med. 1920;v.13(Sect Hist Med):1-15.
Dyková I, Lom J. Histopathology of protistan and myxozoan infections in fishes. Academia; 2007:219.
Einszporn-Orecka T. Flagellates Spironucleus anguillae sp. n. parasites of eel (Anguilla anguilla L.). Acta Protozoologica. 1979;18:237-241.
Fard MRS, Jørgensen A, Sterud E, Bleiss W, Poynton SL. Ultrastructure and molecular diagnosis of Spironucleus salmonis (Diplomonadida) from rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss in Germany. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms. Mar 29 2007;75(1):37-50.
Ferguson HW, Moccia RD. Disseminated hexamitiasis in Siamese fighting fish. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association. 1980;177:854-857.
Ferguson HW. Scanning and transmission electron microscopical observations on Hexamita salmonis (Moore, 1922) related to mortalities in rainbow trout fry Salmo gairdneri Richardson. J Fish Dis. 1979;2:57-67.
Fjær MA. Pukkellaks (Oncorhynchus gorbuscha) tatt på Vestlandet. - Hvilke parasitter og infeksjoner bærer de på? MSc thesis, Univ Bergen, Dept Biosciences. 2019
Furuset A. Parasitt kostet lakseselskapet 900 mill. IntraFish Publisert 22 februar 2024, kl 1102. 2024;
Grupcheva GI, Golemansky VG, Lom J, Dykova I, Pavlaskova M. Protozoan parasites of the fish in some Bulgarian reservoirs. III. Ichthyoparasiting fauna in the "Dospat" reservoir. Acta Zool Bulg. 1986;31:37-41.
Guo FC. Spironucleus spp. and experimental spironucleosis in salmonids. University of Guelph; 2006.
Guo FC, Woo PTK. Detection and quantification of Spironucleus barkhanus in experimentally infected Atlantic salmon Salmo salar. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms. 2004;61:175-178.
Guo FC, Woo PTK. Experimental infections of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar with Spironucleus barkhanus. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms. 2004;61:59-66.
Guz L, Puk K. First molecular identification of Spironucleus salmonis (Diplomonadida) from diseased rainbow trout Oncorchynchus mykiss in Poland. Med Weter. 2015;71(8):497-499.
Hare GM, Frantsi C. Abundance and potential pathology of parasites infecting salmonids in Canadian maritime hatcheries. J Fish Res Bd Can. 1974;31:1031-1036.
Helsø M. Miljøoverlevelse hos Spironucleus salmonicida - parasitten som forårsaker systemisk spironukleose hos oppdrettslaks. MSc Thesis, BiO, Univ Bergen, . 2024;
Hoffmann GL. Parasites of North American freshwater fishes. 2 ed. Comstock Publishing Associates; 1999:539.
Imamovic V. Parasites and parasitoses in the fish in some salmonid hatcheries in Bosnia-Hercegovina I. Ichthyobodiosis and hexamitosis. Veterinaria. 1986;35:47-66.
Jackson GA, Livingston RS, Riley LK, Livingston BA, Franklin CL. Development of a PCR assay for the detection of Spironucleus muris. Journal of the American Association for Laboratory Animal Science. 2013;52(2):165-170.
Jerlström-Hultqvist Jea. Hydrogenosomes in the diplomonad Spironucleus salmonicida. Nature Communications. 2013;4:2493:9 p. doi:DOI: 10.1038/ncomms3493
Johansen L-H, Brenne H. Effekten av ulike desinfeksjonsstrategier på Spironucleus salmonicida. AP 2.1. Nofima Rapport. 2024;2024(25)
Jørgensen A, Alfjorden A, Henriksen K, Sterud E. Phylogenetic analysis of the SSU rRNA gene from the piscine diplomonad Spironucleus torosus (Diplomonadida : Hexamitinae). Folia Parasitologica. 2007;54:277-282.
Jørgensen A, Sterud E. The marine pathogenic genotype of Spironucleus barkhanus from farmed salmonids redescribed as Spironucleus salmonicida n. sp. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2006;53:531-541.
Jørgensen A, Sterud E. Phylogeny of Spironucleus (Eopharyngia : Diplomonadida : Hexamitinae). Protist. 2007;158:247-254.
Jørgensen A, Torp K, Bjørland MA, Poppe TT. Wild Arctic char Salvelinus alpinus and trout Salmo trutta: hosts and reservoir of the salmonid pathogen Spironucleus salmonicida (Diplomonadida; Hexamitidae). Diseases of Aquatic Organisms. 2011;97(1):57-63. doi:Doi 10.3354/Dao02404
Karlsbakk E, Fjær MA, Moore LJ, Skaala Ø, Madhun AS. Pukkellaks og villaks, patogener og parasitter - hva vet vi? Norsk Fiskeoppdrett. 2020;2020(1):60-63.
Karlsbakk E, Sandlund N, Austgulen MH, et al. Verter og vektorer i sjø for Spironucleus salmonicida, mikroparasitten som forårsaker systemisk spironucleose i oppdrettslaks. Abstract, Frisk Fisk 2025 Tromsø. 2025;
Kayis S, Ozcelep T, Capkin E, Altinok I. Protozoan and metazoan parasites of cultured fish in Turkey and their applied treatments. The Israeli Journal of Aquaculture – Bamidgeh. 2009;61(2):93-102.
Kent ML, Ellis J, Fournie JW, Dawe SC, Bagshaw JW, Whitaker DJ. Systemic hexamitid (Protozoa: Diplomonadida) infection in seawater pen-reared chinook salmon Oncorhynchus tshawytscha. Dis Aquat Org. 1992;14:81-89.
Kent ML. Protozoa and Myxozoa. In: Kent ML, Poppe TT, eds. Diseases of seawater netpen-reared salmonid fishes. Fisheries & Oceans; 1998:49-67.
Kirjusina M, Vismanis K. Checklist of the parasites of fishes of Latvia. FAO Fisheries Technical Paper. 2007;369/3:106 p.
Konovalov SM. Differentiation of local populations of sockeye salmon Oncorhynchus nerka (Walbaum). University of Washington, Publications in Fisheries, new series (Sagen, LV, transl). 1975;6:1-290.
Kristmundsson A, Richter SD. Parasites of resident Arctic charr, Salvelinus alpinus, and brown trout, Salmo trutta, in two lakes in Iceland. Icel Agric Sci. 2009;22:5-18.
Kulda J, Lom J. Remarks on the diplomastigine flagellates from the intestine of fishes. Parasitology. 1964;54:753-762.
Kunstyr I. Infectious form of Spironucleus (Hexamita) muris: banded cysts. Laboratory Animals. 1977;11:185-188.
Kvamme BO, Mæhle S, Berg-Rolness H, et al. Utprøving av fem ulike Spironucleus salmonicida smittemodellar for post-smolt laks i sjøvatn. Rapport fra havforskningen. 2025;2025(25)
Kyst.no. Parasitt har gitt betydelige tap i form av dødelighet og destruksjon av fisk - FHF lyser nå ut midler. Kyst.no. Tirsdag 18. oktober 2022 - 14:17
Lavier G. Sur la structure des Flagellés du genre Hexamita Duj. C R Soc Biol. 1936;121:1177-1181.
Lavier G. Sur quelques flagelles intestinaux de Poissons marins. Ann Parasitol. 1936;14(3):278-289.
Leitsch D, Williams CF, Hrdy I. Redox pathways as drug targets in microaerophilic parasites. Trends in Parasitology. 2018;34(7):576-586.
Lie K-I, Wisløff H, Alarcon M, Nylund S. Spironukleose hos atlantisk laks. Norsk Veterinærtidsskrift. 2022;134(6):400-401.
Lloyd D, Chapman A, Ellis JE, et al. Oxygen levels are key to understanding “anaerobic” protozoan pathogens with micro-aerophilic lifestyles. Advances in Microbial Physiology. 2021;79:163-240.
Lloyd D, Millet CO, Williams CF, et al. Functional imaging of a model unicell: Spironucleus vortens as an anaerobic but aerotolerant flagellated protist. Advances in Microbial Physiology. 2020;76:41-79.
Lloyd D, Williams CF. Comparative biochemistry of Giardia, Hexamita and Spironucleus: Enigmatic diplomonads. Molecular & Biochemical Parasitology. 2014;197:43–49.
Lofnes A. Spironucleus salmonicida – histopatologi og vevstropisme i ulike vertsarter. MSc thesis, BiO, UiB. 2025;
Lom J, Dyková I. Protozoan parasites of fishes. vol 26. Developments in Aquaculture and Fisheries Science. Elsevier; 1992:315.
Lom J, Dyková I. Protozoární paraziti uzitkovych ryb [Protozoan parasites of commercial fish]. Vydal. Cesky rybarsky svaz ve Statnim zemedelskem nakladatelstvi [Czech Fishermen's Association in the State Agricultural Publishing House]; 1989:102.
Love MS, Moser M. A checklist of parasites of California, Oregon, and Washington marine and estuarine fishes. NOAA Technical Report NMFS SSRF. 1983;777:1-576.
Mankhakhet Sea. Diplomonad flagellates of some ornamental fish cultured in Thailand. Songklanakarin J Sci Technol. 2012;34(5):487-494.
Markeng D. Spironukleose i Finnmark. Aquavisa. 2001;1(3):2-3.
Miller KMea, Gardner IA, Vanderstichel R, et al. Report on the performance evaluation of the Fluidigm BioMark platform for high-throughput microbe monitoring in salmon. Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat (CSAS), Research Document 2016/038, Pacific Region. 2016;2016(038)
Millet C. Growth, metabolism, ultrastructure and chemotherapy of Spironucleus vortens. PhD Thesis, Cardiff University. 2009;
Millet COM, Lloyd D, Coogan MP, Rumsey J, Cable J. Carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism of Spironucleus vortens. Experimental Parasitology. 2011;(129):17–26.
Millet COM, Williams CF, Hayes AJ, Hann AC, Cable J, Lloyd D. Mitochondria-derived organelles in the diplomonad fish parasite Spironucleus vortens. Experimental Parasitology. 2013;135:262–273.
Mizuno K, Urawa S, Katsumata Y, Morishita T, Minowa Y, Ban M. Quantitative analysis of diplomonad flagellate Spironucleus salmonis infection in intestines of hatchery and wild salmonid fishes in Hokkaido. Fish Pathology. 2020;55(3):61-70. doi:doi.org/10.3147/jsfp.55.61
Mizuno S, Urawa S, Katsumata Y, Morishita T, Ban M. Ultrastructural and molecular phylogenetic identification of the diplomonad flagellate Spironucleus salmonis infecting hatchery-reared salmonid fishes in Hokkaido. Fish Pathol. 2020;55(1):8-17.
Mo TA, Poppe TT. Hexamitose i nordnorske oppdrettsanlegg: en tilfeldighet eller et nytt alvorlig problem. Norsk Fiskeoppdrett. 1992;(11A):48-50.
Mo TA, Poppe TT, Appleby C. Kohabiteringsforsøk med fire ulike arter laksefisk og en encellet parasitt i slekten Hexamita. Norsk Veterinærtidsskrift. 1993;105(3):349-353.
Mo TA, Poppe TT, Iversen L. Systemic hexamitosis in salt-water reared Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Bull Eur Ass Fish Pathol. 1990;10(3):69-70.
Mo TA [Moe TA, lapsus), Poppe T, Håstein T. Encellede parasitter (Protozoa). In: Poppe TT, ed. Fiskehelse Sykdommer, behandling, forebygging. John Griegs Forlag; 1990:228-239.
Molnár K. Data on the “octomitosis” (spironucleosis) of cyprinids and aquary fishes. Acta Vet Acad Sci Hungaricae. 1974;24:99-106.
Moore E. Octomitus salmonis, a new species of intestinal parasite in trout. Trans Am Fish Soc. 1922;52:74-97.
Moore E. The life-history of Octomitus salmonis, an intestinal flagellate of trout. Anat Rec. 1923;26:358-359.
Moroff T. Beitrag zur Kenntnis einiger Flagellaten. Arch Protistenkd. 1904;3:69-106.
Morrison CM. Histology of the Atlantic Cod, Gadus morhua: An Atlas. Part one. Digestive tract and associated organs. Can Spec Publ Fish Aquat Sci 1987;98:219 p.
NVI. Fiskehelserapporten 2022. Veterinærinstituttet rapportserie. 2023;2023(5a)
NVI. Fiskehelserapporten 2023. Veterinærinstituttet rapportserie. 2024;2024(8a)
Ogut H, Parlak R. Hexamitiasis leads to lower metabolic rates in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum) juveniles. J Fish Dis. 2014;37:1013-1020.
Paull GC, Matthews RA. Spironucleus vortens, a possible cause of hole-in-the-head disease in cichlids. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms. 2001;45:197-202.
Pazooki J, Masoumian M. Synopsis of the parasites in Iranian freshwater fishes. Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences. 2012;11(3):570-591.
Petrushevskii GK, Pozdnyakova (Vikhrova) MN, Shul'man SS. The parasites of fish from Braslav Lakes in Belorussia. In: Petrushevskii GK, ed. Parasites and diseases of fish. Otdel Rybnoi Promyshlennosti Gosplana RSFSR; 1957:336-338. vol. Bulletin of the All/Union Scientific Research Institute of Lake and River Fisheries.
Poppe TT, Mo TA, Iversen L. Disseminated hexamitosis in sea-caged Atlantic salmon Salmo salar. Dis Aquat Org. 1992;14:91-97.
Poppe TT, Mo TA, Torgersen Y. Effekt av ulike behandlingsmidler på en encellet parasitt i slekten Hexamita isolert fra oppdrettslaks. Norsk Veterinærtidsskrift. 1993;105:835-838.
Poppe TT, Mo TA. Hexamita - parasitten gir sykdom hos oppdrettslaks i sjø. Norsk Fiskeoppdrett. 1992;1992(4):26-28.
Poppe TT, Mo TA. Systemic, granulomatous hexamitosis of farmed Atlantic salmon: Interaction with wild fish. Fisheries Research. 1993;17:147-152.
Poynton SL. Distribution of the flagellate Hexamita salmonis Moore, 1922 and the microsporidian Loma salmonae Putz, Hoffman and Dunbar, 1965 in brown trout, Salmo trutta L., and rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson, in the River Itchen (U.K.) and three of its fish farms. J Fish Biol. 1986;29:417-429.
Poynton SL, Fard MRS, Jenkins J, Ferguson HW. Ultrastructure of Spironucleus salmonis n. comb. (formerly Octomitus salmonis sensu Moore 1922, Davis 1926, and Hexamita salmonis sensu Ferguson 1979), with a guide to Spironucleus species. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms. 2004;60:49-64.
Poynton SL, Fraser W, Francis-Floyd R, Rutledge P, Reed P, Nerad TA. Spironucleus vortens n. sp. from the freshwater angelfish Pterophyllum scalare: morphology and culture. J Euk Microbiol. 1995;42(6):731-742.
Poynton SL, Morrison CM. Morphology of diplomonad flagellates: Spironucleus torosa n. sp. from Atlantic cod Gadus morhua L., and haddock Melanogrammus aeglefinus (L.) and Hexamita salmonis Moore from brook trout Salvelinus fontinalis (Mitchill). J Protozool. 1990;37(5):369-383.
Poynton SL, Sterud E. Guidelines for species descriptions of diplomonad flagellates from fish. Journal of Fish Diseases. 2002;25:15-31.
Roxström-Lindquist K, Jerlström-Hultqvist J, Jørgensen A, Troell K, Svärd SG, Andersson JO. Large genomic differences between the morphologically indistinguishable diplomonads Spironucleus barkhanus and Spironucleus salmonicida. BMC Genomics. 2010;11(258)
Schmidt W. Untersuchungen über Octomitus intestinalis truttae. Arch Protistenkunde. 1920;40:253-289.
Seligo A. Untersuchungen über Flagellaten. Beiträge zur Biologie der Pflanzen. 1887;4(2):145-180.
Shulman BS, Ieshko EP. Parasite fauna of Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus) and greyling (Thymallus thymallus) in some lakes from northern Finland. Lososevidnye Ryby Vostochnoi Fennoskandii, Petrozavodsk. 2005:195-197.
Skenderovic I, Adrovic A, Jazic A, Zuko A, Hadzimustafic E. Review of freshwater fish parasitofauna of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Biologia. 2020;doi:https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00565-0
Sommerhaug E. Kultivering av mikroparasitten Hexamita sp. in vitro og in vivo i atlantisk laks (Salmo salar), og påvisning av antistoffaktivitet mot parasitten i atlantisk laks. cand. scient. Tromsø; 1995.
Stairs CW et al. Oxygen induces the expression of invasion and stress response genes in the anaerobic salmon parasite Spironucleus salmonicida. BMC Biology. 2019;17:19
Sterud E, Poppe T, Bornø G. Intracellular infection with Spironucleus barkhanus (Diplomonadida : Hexamitidae) in farmed Arctic char Salvelinus alpinus. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms. 2003;56:155-161.
Sterud E, Poppe T, Bornø G. Systemisk infeksjon med Spironucleus barkhanus hos sjørøye i oppdrett. Norges Forskningsråd; 2002:46.
Sterud E, Poppe TT, Bornø G. Systemic and intracellular infection with Spironucleus barkhanus in farmed Arctic char, Salvelinus alpinus. 6 ISAFP Bloemfontein, South Africa (Sixth International Symposium on fish Parasites, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein, South Africa). 2003:31.
Sterud E, Poppe TT, Larsen T, Iversen L. Men Spironucleus var ikke død. Norsk Fiskeoppdrett. 2002;Kyst.no 13/06/2002 (?):38-40.
Timur G, Karatas S, Akayli T, Ercan MD, Yardimci RE. A histopathological study of hexamitiasis in farmed rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fry in Turkey. Bulletin of the European Association of Fish Pathologists. 2009;29(3):104-108.
Tojo JL, Santamarina MT. Oral pharmacological treatments for parasitic diseases of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. I: Hexamita salmonis. Dis Aquat Org. 1998;33:51-56.
Turovskij A. Parasitofauna of fish in the southern Gulf of Finland. Finnish Fish Res. 1985;6:106-111.
Uldal A. Life cycle observations on Hexamita salmonis from rainbow trout intestine. In vitro studies. Bull Eur Ass Fish Pathol. 1996;16(4):112-114.
Uzmann JR. The Hexamita (=Octomitus) problem: a preliminary report. Progr Fish Cult. 1963;25(3):141-143.
Uzmann JR, Hayduk SH. In vitro culture of the flagellate protozoan Hexamita salmonis. Science. 1963;140:290-292.
Uzmann JR, Paulik GJ, Hayduk SH. Experimental hexamitiasis in juvenile coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) and steelhead trout (Salmo gairdneri). T Am Fish Soc. 1965;94(1):53-61.
Vickerman K. Phylum Zoomastigina Class Diplomonadida. In: Margulis L, Corliss JO, Melkonian M, Chapman DJ, eds. Handbook of Protoctista: The Structure, Cultivation, Habitats and Life Histories of the Eukaryotic Microorganisms and their Descendants. Jones and Bartlett Publishers; 1990:200-210.
Vinnichenko LN, Zaika VE, Timofeev VA, Shtein GA, Shulman SS. Parasitic Protozoa of fishes from the Amur river basin. Parazitol Sbornik. 1971;25:10-40.
Williams CF. Life cycle, biochemistry and chemotherapy of Spironucleus vortens. Thesis, PhD, School of Biosciences, Cardiff University. 2013;
Williams CF, Lloyd D, Kolarich D, et al. Disrupted intracellular redox balance of the diplomonad fish parasite Spironucleus vortens by 5-nitroimidazoles and garlic-derived compounds. Veterinary Parasitology. 2012;190:62– 73.
Williams CF, Lloyd D, Poynton SL, Jorgensen A, Millet COM, Cable J. Spironucleus species: Economically-important fish pathogens and enigmatic single-celled eukaryotes. Journal of Aquaculture, Research & Development. 2011;2011(S2):13 p. doi:10.4172/2155-9546.S2-002
Williams CF, Vacca AR, Lloyd D, et al. The redox-active drug metronidazole and thiol-depleting garlic compounds act synergistically in the protist parasite Spironucleus vortens. Molecular & Biochemical Parasitology. 2016;206:20–28.
Williams CF, Vacca AR, Lloyd D, Schelkle B, Cable J. Non-invasive investigation of Spironucleus vortens transmission in freshwater angelfish Pterophyllum scalare. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms. Sep 3 2013;105(3):211-223. doi:Doi 10.3354/Dao02618
Williams CF, Yarlett N, Aon MA, Lloyd D. Antioxidant defences of Spironucleus vortens: Glutathione is the major non-protein thiol. Molecular & Biochemical Parasitology. 2014;196:45–52.
Wiśniewska MM, Salomaki ED, Silberman JD, et al. Expanded gene and taxon sampling of diplomonads shows multiple switches to parasitic and free-living lifestyle. BMC Biology. 2024;22:217doi:10.1186/s12915-024-02013-w
Woo PTK, Poynton SL. Diplomonadida, Kinetoplastida and Amoebida (Phylum Sarcomastigophora). In: Woo PTK, ed. Fish Diseases and Disorders Vol I Protozoan and metazoan infections. CAB International; 1995:27-96.
Wood AM, Smith HV. Spironucleosis (Hexamitiasis, Hexamitosis) in the ring-necked pheasant (Phasianus colchicus): Detection of cysts and description of Spironucleus meleagridis in stained smears. Avian Diseases. 2005;49(1):138-143.
Wood JW. Diseases of Pacific salmon; Their prevention and treatment. 3 ed. State of Washington, Department of Fisheries, Hatchery Division; 1979:82.
Xu F, Jerlström-Hultqvist J, Einarsson E, Astvaldsson A, Svärd SG, Andersson JO. The genome of Spironucleus salmonicida highlights a fish pathogen adapted to fluctuating environments. PLoS Genet. 2014;10(2):e1004053. doi:doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004053
Xu F, Jiménez-González A, Kurt Z, Ástvaldsson Á, Andersson JO, Svärd SG. A chromosome-scale reference genome for Spironucleus salmonicida. Scientific Data. 2022;9:585doi:10.1038/s41597-022-01703-w
Zaika VE. The parasitofauna of fish in Lake Baikal. Izdatel’stvo "Nauka"; 1965:106.